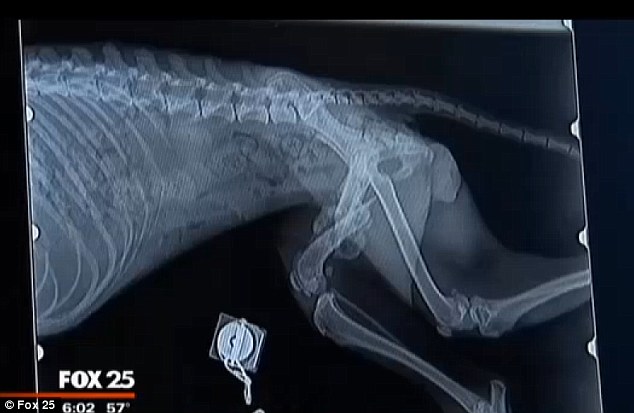
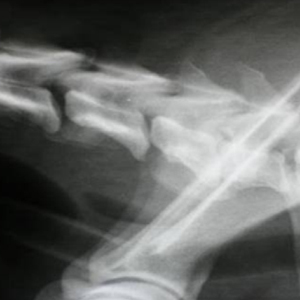
Although it may not seem like it, dogs suffer from many of the ailments that humans experience. From a simple cold to osteoarthritis, through hernias. As in humans, those suffered by dogs can have varying severity. In addition, hernias in dogs can be of four types: inguinal, diaphragm, umbilical and disc.
In any of the four cases, it is very important to diagnose them correctly as soon as possible. In this way, the appropriate treatment can be applied to the animal to relieve its discomfort. To do this, the main thing is to understand what a hernia is, what it implies and the main types of hernias in dogs.
Hernia in dogs: main types
The hernias of dogs, like those of humans, are lumps and bumps product of the exit of tissue from some organ of its usual position. They are quite painful, and are usually noticeable because the animal has a lump where it should not. A lump that is painful to the touch on many occasions.
As we have mentioned, the main types of hernias in dogs are four. Of these, the two most common are umbilical and disc herniations . The first usually occur when the animal is very young, shortly after birth. They usually start when the mother of a puppy incorrectly cuts the umbilical cord that joins him to him. When this happens they do not have a navel left as it happens with humans. But it is noticeable in an area that there has been a union with the mother.
In that area, if a hernia has formed, there will be a lump. Do not try to push it into the animal, because it can be painful. The solution to this hernia, and in general to all, is a surgical intervention to eliminate it.
The second most common type of hernia in dogs is herniated disc. Generally, it has its origin in a fall or a blow, which cause a rupture or inflammation of the intervertebral discs of the dog’s spine . However, in older dogs it may simply be due to the deterioration of the discs.
This hernia, in addition to being very painful, can generate mobility problems for dogs. These will be greater the more advanced and severe the hernia. In many cases, the solution will be surgery, but since it involves certain risks, it is the veterinarian who will have to assess if it is worth it. Meanwhile, you can relieve their pain with painkillers and anti-inflammatories. And in case the hernia is very serious and mobility is impaired, you can help him recover it with an adaptable dog wheelchair .
Inguinal and abdominal hernias in dogs
The other two types of hernia in dogs are less common. But equally painful for the animal. They are inguinal hernias and diaphragm hernias. The first are formed in the inguinal canal, a duct located between the muscles of the abdomen.
These types of hernias, which have the appearance of a mass of tissues, can become quite large. Therefore, as soon as they are detected, it is advisable to eliminate them by surgery, and this will probably be indicated by the veterinarian.
As for hernias of the diaphragm, they can cause serious health problems to the affected dog. This hernia, which is usually internal, often develops into the dog’s body. This is dangerous, as it can displace your organs. And it makes that many times, its symptoms are completely different from those of the rest of hernias.
Among them, the dog may have shortness of breath and irregularity in the heartbeat. Also vomiting or diarrhea if it affects the stomach or intestine. In addition, you may notice strange movements in the dog’s abdomen. This type of hernia is quite serious, and must be intervened as soon as possible to correct it.